Stack Data structure | Stack DS | Satack
Stack is a data structure which has these followings characteristics:
- It has only one terminal from where data is insert or get.
- The process of inserting the data in the stack data structure is called push. (Push = insert)
- The process of getting data from the stack data structure is called pop. (Pop = Get)
- The LIFO (last in first out) methodology is used in the stack data structure.
- There is sequential access in the stack data structure.
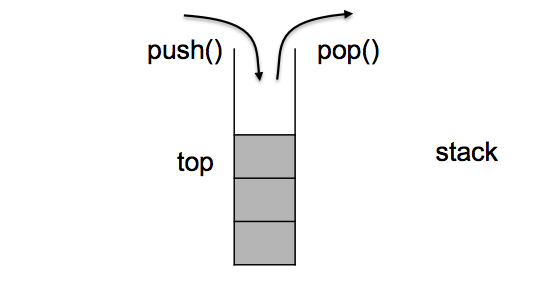
Pictorial demo. of Push and Pop
Pictorial demo. of Push and Pop
Pictorial demo. of Push and Pop
Stack in java:
Explanation
Explanation
The Java Core API has a stack class in the package
java.util but you should avoid it since it subclassesVector and thus has a bunch of non-stack operations (this is a major design flaw in the library), and it is (perhaps unnecessarily) synchronized making it slow (though always thread-safe).
Regardless, you should learn how to build a stack ADT from scratch, because:
- This is the only way for you to really learn how stacks work
- You need coding practice, especially with linked structures
- You need to know how to code things up when you find yourself in a very restrictive environment that doesn't have a collections library.
Operations
push(x): add an item on the toppop: remove the item at the toppeek: return the item at the top (without removing it)size: return the number of items in the stackisEmpty: return whether the stack has no items
- Stacks of plates
- Trains
- Vending Machines
- Expression Evaluation
- Matching delimiters
- Navigating a maze
- Map coloring
- Many more examples
Example program (by array)
import java.util.*;
/* Class arrayStack */
class arrayStack
{
// basic storage array
protected int arr[];
protected int top, size, len;
/* Constructor for arrayStack */
public arrayStack(int n)
{
size = n;
len = 0;
//giving the size to array
arr = new int[size];
top = -1;
}
/* Function to check if stack is empty */
public boolean isEmpty()
{
// if there is no increment in the top (nothing add to the array)
return top == -1;
}
/* Function to check if stack is full */
public boolean isFull()
{
return top == size -1 ;
}
/* Function to get the size of the stack */
public int getSize()
{
return len ;
}
/* Function to check the top element of the stack */
public int peek()
{
if( isEmpty() )
// for exception handling
throw new NoSuchElementException("Underflow Exception");
return arr[top];
}
/* Function to add an element to the stack */
public void push(int i)
{
if(top + 1 >= size)
// for exception handling
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Overflow Exception");
if(top + 1 < size )
arr[++top] = i;
len++ ;
}
/* Function to delete an element from the stack */
public int pop()
{
if( isEmpty() )
throw new NoSuchElementException("Underflow Exception");
len-- ;
return arr[top--];
}
/* Function to display the status of the stack */
public void display()
{
System.out.print("\nStack : ");
if (len == 0)
{
System.out.print("Empty\n");
return ;
}
// show only those who are push and not pop(main logic)
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
/* Class StackImplement */
public class Stack
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Stack Test\n");
System.out.println("Enter Size of Integer Stack ");
int n = scan.nextInt();
/* Creating object of class arrayStack */
arrayStack stk = new arrayStack(n);
/* Perform Stack Operations */
char ch;
do{
System.out.println("\n\n\n----------Stack Operations----------");
System.out.println("1. push");
System.out.println("2. pop");
System.out.println("3. peek");
System.out.println("4. check empty");
System.out.println("5. check full");
System.out.println("6. size");
int choice = scan.nextInt();
switch (choice)
{
case 1 :
System.out.println("Enter integer element to push");
try
{
stk.push( scan.nextInt() );
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Error : " + e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 2 :
try
{
System.out.println("Popped Element = " + stk.pop());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Error : " + e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 3 :
try
{
System.out.println("Peek Element = " + stk.peek());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Error : " + e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 4 :
System.out.println("Empty status = " + stk.isEmpty());
break;
case 5 :
System.out.println("Full status = " + stk.isFull());
break;
case 6 :
System.out.println("Size = " + stk.getSize());
break;
default :
System.out.println("Wrong Entry \n ");
break;
}
/* display stack */
stk.display();
System.out.println("\nDo you want to continue (Type y or n). \n");
// for check what is character at oth index of the above enter string
ch = scan.next().charAt(0);
} while (ch == 'Y'|| ch == 'y');
}
}



nice dear good job
ReplyDeleteThanks...
Deletekeep visiting......
Respected bro please do some work of data structure in C++
ReplyDelete